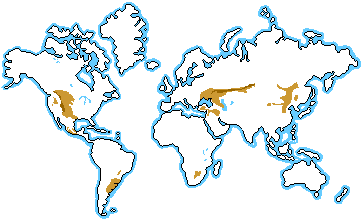
Grasslands are generally open and continuous, fairly flat areas of grass.
They are often located between temperate forests at high latitudes and deserts at subtropical latitudes. Grasses vary in size from 2.1 m (7 ft) tall with roots extending down into the soil 1.8 m (6 ft), to the short grasses only a few mm. tall.
Grasslands receive about 500 to 900 mm (about 20 to 35 in) of rain per year
compared to deserts, which receive less than 300 mm (12 in) and tropical
forests, which receive more than 2,000 mm.
While temperatures are often extreme in some grasslands, the average temperatures are about -20 to 30 degrees Celsius. Tropical grasslands have dry and wet seasons that remain warm all the time. Temperate grasslands have cold winters and warm summers with rain or some snow.
Tropical and subtropical grasslands are classified with tropical and subtropical savannas and shrublands as the tropical and subtropical grasslands, savannas, and shrublands biome.
Temperate grasslands are mid-latitude grasslands, They are classified with temperate savannas and shrublands as the temperate grasslands, savannas, and shrublands biome.Temperate grasslands are the home to many large herbivores.
Some of these include bison, gazelles, zebras, rhinoceroses, and wild horses. Carnivores like lions, wolves and cheetahs are also found in temperate grasslands. Other animals of this region include: deer, prairie dogs, mice, jack rabbits, skunks, coyotes, snakes, fox, owls, badgers, blackbirds, grasshoppers, meadowlarks, sparrows, quails, and hawks.
Flooded grasslands are grasslands that are flooded seasonally or year-round, They are classified with flooded savannas as the flooded grasslands and savannas biome, which occurs mostly in the tropics and subtropics.
Montane grasslands are high-altitude grasslands located on high mountain ranges around the world, They are part of the montane grasslands and shrublands biome.
Xeric grasslands or desert grasslands are sparse grasslands located in deserts and xeric shrublands ecoregions.